How GCC Cars Handle Cold European Weather & Snow: Complete Winterisation Guide

GCC-spec vehicles are engineered for extreme heat and desert environments, where cooling efficiency and dust resistance are critical. In contrast, European winters introduce freezing temperatures, snow, and salt-treated roads. These conditions expose gaps in vehicles designed primarily for hot climates.
 AI Quick Summary
AI Quick Summary
GCC-spec vehicles, engineered for extreme heat, encounter significant mechanical, safety, and legal risks when operated in European winters due to fundamental design differences that neglect cold-weather priorities. Successful and safe operation requires extensive winterization, addressing critical areas such as engine oil, battery, antifreeze, fuel gelling, corrosion protection, and legally mandated winter tires.
This summary was generated by AI using this article’s content.Read Next
The key issue is not vehicle quality, but climate mismatch. With the right preparation, GCC-spec vehicles can operate reliably in Europe. Without it, owners face mechanical, safety, and legal risks.
What Are the Main Design Differences Between GCC and EU Vehicles?
The core conflict lies in opposite engineering priorities.
GCC vehicle design focuses on:
- High-capacity cooling systems
- Larger radiators and oil coolers
- Powerful air conditioning units
- Dust and sand filtration
EU vehicle design focuses on:
- Strong cabin heating systems
- Fast windscreen defrosting
- Cold-start reliability
- Winter-tested fluids and materials
Because GCC vehicles prioritise heat rejection, they often struggle to retain warmth in freezing conditions, leading to poor heating performance and reduced comfort.
How Does Cold Weather Affect Engine Oil in GCC Vehicles?
Engine oil is one of the most critical winter weaknesses.
GCC vehicles usually run thicker oil grades suited for high temperatures. In cold weather, this oil thickens further, restricting flow and increasing strain on the starter motor during cold starts.
Winter preparation requires:
- Switching to 0W-30 or 0W-40 synthetic oil
- Improving cold-start lubrication
- Reducing engine wear during ignition
Without this change, engine damage accumulates rapidly in winter use.
Why Do Batteries Fail More Often in European Winters?
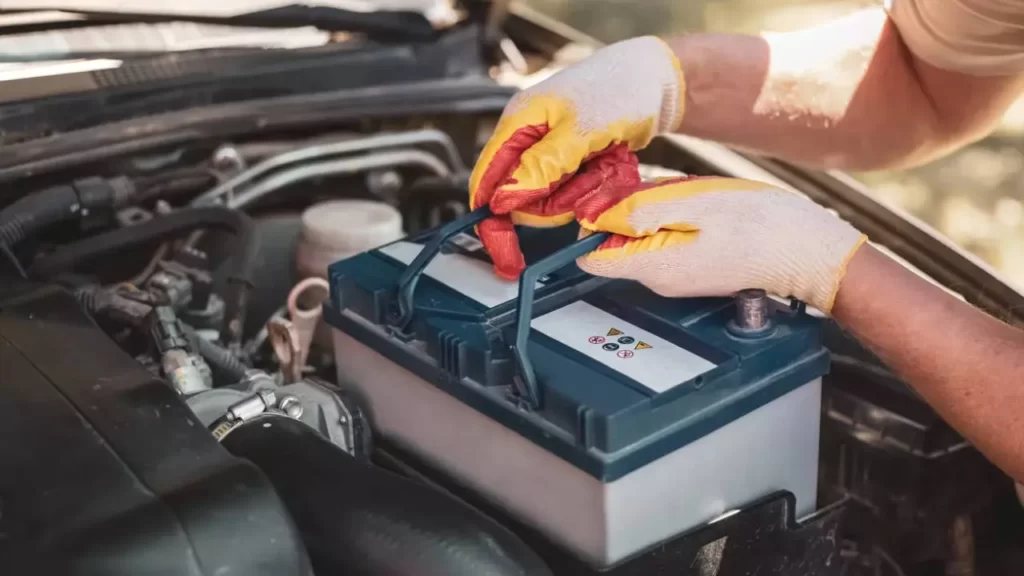

Cold weather significantly reduces battery output. At 0°C, a battery can lose around 30% of its starting power. This becomes a serious problem when combined with:
- Thickened engine oil
- Increased starter motor resistance
- Batteries already weakened by desert heat
Recommended actions:
- Test battery voltage and cold cranking amps
- Replace batteries older than 3–4 years
- Clean terminals and check charging systems
Battery failure is one of the most common winter breakdown causes.
Are Diesel Engines at Risk of Fuel Gelling?
Yes. Diesel engines face a higher winter risk. Diesel fuel contains wax that crystallises in low temperatures. This blocks fuel filters and prevents fuel from reaching the engine.
To prevent diesel gelling:
- Use European winter diesel
- Add cold-flow improver additives
- Install fuel or engine block heaters
Without these measures, diesel GCC vehicles may fail to start after a cold night.
Is Antifreeze in GCC Vehicles Sufficient for Europe?
In many cases, no. GCC vehicles often use coolant mixtures designed only for mild cold. European winters can exceed these limits, especially in Alpine and Nordic regions.
Winter coolant preparation includes:
- Testing freeze protection with proper tools
- Using at least a 50/50 antifreeze mix
- Increasing concentration for severe cold regions
Inadequate antifreeze can cause catastrophic engine damage.
How Does Road Salt Damage GCC Vehicles?
European road salt creates an aggressive corrosion environment. GCC corrosion protection is designed for humidity and airborne salt, not constant exposure to salt slurry on winter roads.
High-risk areas include:
- Exhaust systems
- Brake lines
- Suspension components
- Electrical connectors
- Structural frame sections
Effective protection methods:
- Professional underbody coatings
- Cavity wax treatments
- Regular undercarriage washing
These measures can extend vehicle life by several years.
Are Winter Tyres Legally Required in Europe?
In most countries, yes. Summer or all-terrain tyres harden in cold weather and provide poor grip on snow and ice.
European winter tyre rules typically require:
- Tyres with the Alpine snowflake symbol
- Winter tyres from November to March
- Snow chains in mountainous regions
Failure to comply can result in fines, vehicle bans, or insurance issues.
What Is the Role of an Engine Block Heater?
Engine block heaters are one of the most effective winter upgrades. They warm the engine oil or coolant before starting, reducing wear and improving reliability.
Benefits include:
- Easier cold starts
- Reduced engine stress
- Lower emissions
- Improved fuel efficiency in winter
They are especially important for diesel vehicles and extreme cold regions.
Do Diesel Glow Plugs Need Special Attention?
Yes, particularly in winter. Glow plugs preheat combustion chambers. Faulty plugs may still work in mild weather but fail in cold conditions.
Best practice includes:
- Professional inspection before winter
- Replacing worn glow plugs
- Allowing full pre-heating before starting
This prevents failed starts and starter motor damage.
Why Is Winter Washer Fluid Essential?
Standard washer fluid freezes at 0°C, making it useless in winter. Frozen washer systems reduce visibility and increase accident risk.
Winter washer fluid features:
- Lower freezing points
- Higher alcohol content
- Reliable spray performance in snow and ice
Never use engine antifreeze in washer systems, as it damages components.
Is Winterising a GCC Vehicle Cost-Effective?
Yes, when compared to potential damage.
Typical winterisation costs:
- AED 8,000 to AED 14,800 for full preparation, depending on vehicle size and winter severity
Potential risks without preparation:
- Engine freeze damage
- Brake system failure
- Severe corrosion
- Insurance claim rejection
From both safety and financial perspectives, winterisation is a smart investment.
Can GCC Vehicles Work in European Winter?
Yes, but only with proper preparation. GCC vehicles are well-built but optimised for heat, not cold. European winter use requires reversing that thermal focus through targeted upgrades.
With correct fluids, tyres, heating systems, and corrosion protection, GCC-spec vehicles can operate safely and reliably across Europe, even in winter. Preparation is not optional—it is essential.
Find the best used cars for sale in the UAE.
Stay tuned to UAE’s most popular auto blog for more information about the latest happenings in all of the Emirates.
FAQs
Can GCC-spec cars be used in European winter?
Yes, GCC-spec cars can be used in European winter if they are properly winterised with correct fluids, winter tyres, corrosion protection, and heating upgrades. Without preparation, reliability and safety risks increase significantly.
Do GCC vehicles need winter tyres in Europe?
Yes, most European countries legally require winter tyres during cold months. GCC vehicles must use tyres with the Alpine snowflake symbol to ensure safety, legal compliance, and valid insurance coverage.
Why do GCC cars struggle in cold weather?
GCC cars are designed for extreme heat, not cold. They prioritise cooling over heat retention, often lacking strong cabin heating, winter-grade fluids, and cold-start optimisation required for freezing temperatures.
Is winterisation of a GCC vehicle expensive?
Winterising a GCC vehicle typically costs between AED 8,000 and AED 14,800, depending on vehicle type and region. This is far cheaper than repairing engine damage, corrosion, or brake failure caused by winter exposure.
What is the most important winter upgrade for GCC cars?
An engine block heater is one of the most important upgrades. It improves cold starting, reduces engine wear, and ensures reliable operation in freezing European winter conditions.











